Are you wondering if eating eggs could be the reason behind your upset stomach or diarrhea? Eggs are a common part of many diets, but for some people, they might trigger digestive discomfort.
You might be asking yourself: Can eggs cause diarrhea? Or do they actually help firm up your stool? Understanding how eggs affect your digestion can help you make better food choices and avoid unpleasant symptoms. You’ll discover why eggs might sometimes cause diarrhea, when they might actually improve your digestion, and what to do if you suspect eggs are upsetting your stomach.
Keep reading to learn how eggs interact with your digestive system and how to enjoy them without worry.
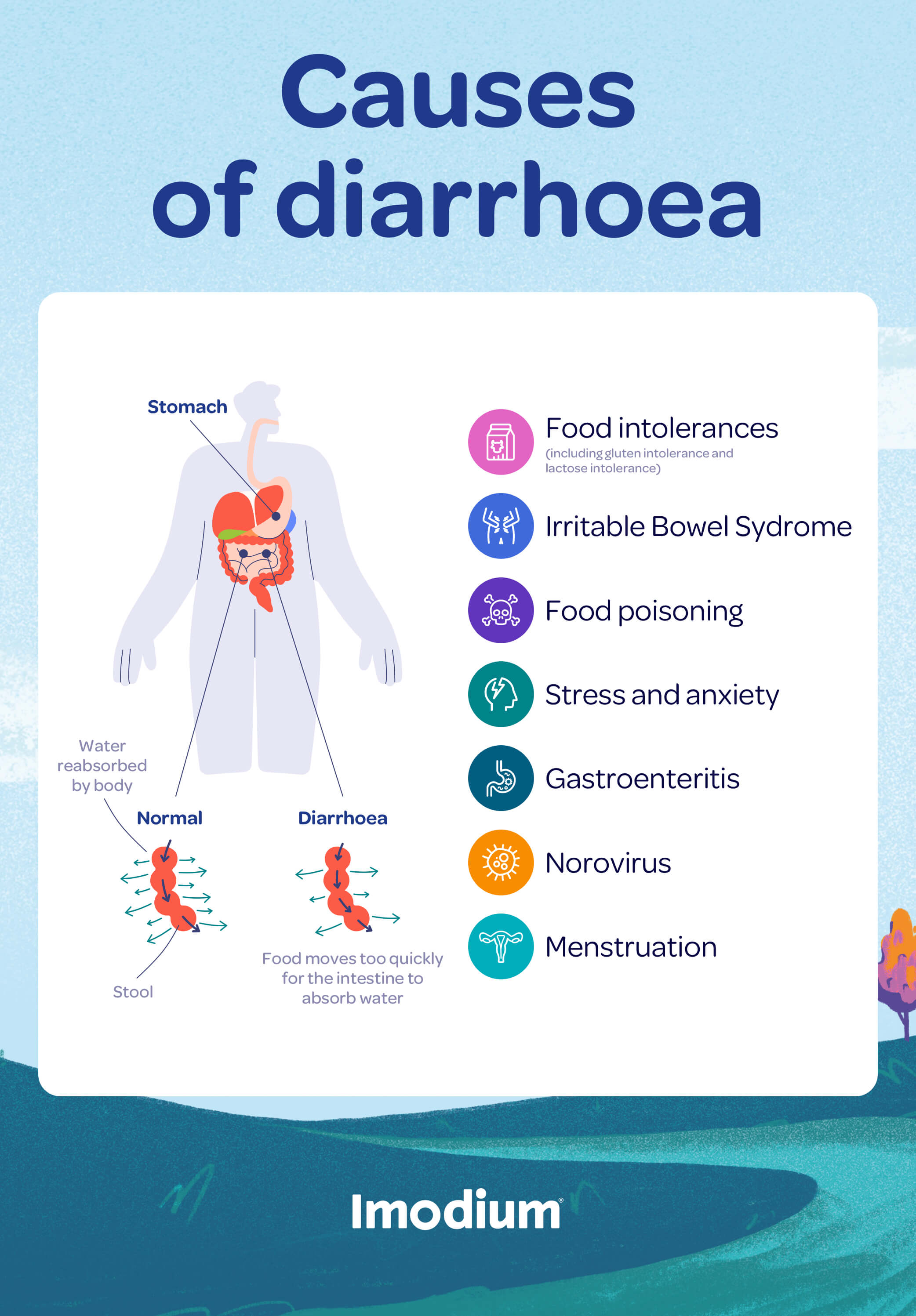
Credit: www.imodium.co.uk
Table of Contents
Eggs And Digestive Effects
Eggs are a common part of many diets worldwide. Understanding their effects on digestion helps clarify if they cause diarrhea or other issues. Eggs contain important nutrients but interact with the digestive system in specific ways. This section explores how eggs affect digestion and bowel movements.
Lack Of Laxative Properties
Eggs do not have laxative effects. They contain almost no dietary fiber, which is key for soft stools. Without fiber, eggs cannot speed up bowel movements or relieve constipation. Eating many eggs alone may actually slow digestion for some people. Eggs are not natural stool softeners or laxatives.
Protein And Fiber Impact
Eggs are rich in protein but low in fiber. Protein helps build and repair body tissues. However, protein alone does not promote regular bowel movements. Fiber adds bulk to stool and helps it pass easily. Since eggs lack fiber, they should be eaten with fiber-rich foods to support digestion. This balance helps avoid constipation and keeps the digestive system healthy.

Credit: www.houndsy.com
Reasons Eggs May Cause Constipation
Eggs are a common food, but they may cause constipation in some people. Understanding why eggs can slow digestion helps manage bowel health. Two main reasons explain this effect.
Low Dietary Fiber
Eggs contain almost no dietary fiber. Fiber is essential for soft, regular bowel movements. Without enough fiber, stools become hard and difficult to pass. Eating many eggs without fiber-rich foods may lead to constipation. Fiber adds bulk and helps move food through the intestines quickly.
High Protein And Fat Content
Eggs have high protein and fat levels. Protein and fat take longer to digest than carbohydrates. This slows down the digestive process. When digestion slows, stool can become dry and hard. A diet high in eggs but low in fiber can increase the risk of constipation. Fat also slows the gut’s movement, adding to the problem.
How Eggs Can Help With Diarrhea
Eggs often get a bad reputation for causing digestive issues. Yet, they can also play a helpful role in managing diarrhea. Their unique nutritional profile supports stool formation and eases gut discomfort. Eggs offer a simple, gentle way to help stabilize digestion during upset stomach days.
Binding Loose Stools
Eggs contain high-quality protein that helps form firmer stools. Protein firms up stool by absorbing water in the intestines. This action reduces stool looseness and frequency. Eating eggs can support the gut lining and slow down bowel movements. Many people find eggs soothing when dealing with diarrhea symptoms.
Suitability For Low-fodmap Diets
Eggs are naturally low in fermentable carbs, known as FODMAPs. Low-FODMAP foods do not cause gas or bloating in sensitive guts. For people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), eggs are safe and easy to digest. Including eggs in a low-FODMAP diet helps maintain nutrition without triggering diarrhea. They provide essential nutrients without upsetting the stomach.
Managing egg-related digestive issues requires simple yet effective strategies. Eggs alone might not cause diarrhea, but how you eat them matters. Combining eggs with the right foods and habits can ease digestion and reduce discomfort.
Pairing Eggs With Fiber-rich Foods
Eggs contain very little fiber, which helps digestion. Eating eggs with fiber-rich foods like vegetables, fruits, or whole grains supports bowel movements. Fiber adds bulk to stools, preventing constipation or diarrhea. For example, add spinach or tomatoes to your eggs. This balance helps your digestive system work smoothly.
Importance Of Hydration
Drinking enough water is key for digestion. Water helps fiber move through your intestines and keeps stools soft. Without enough fluids, fiber cannot do its job well. Aim to drink several glasses of water daily, especially when eating eggs and fiber together. Staying hydrated reduces the risk of digestive upset.
Considering Egg Allergies
Some people have egg allergies, which can cause diarrhea and other symptoms. If you notice digestive problems after eating eggs, an allergy might be the cause. Symptoms can include stomach pain, diarrhea, or skin reactions. Consult a healthcare professional for testing and advice. Avoid eggs if you have an allergy to protect your gut health.
Egg Intolerance Symptoms
Egg intolerance can cause various symptoms that affect your daily life. These symptoms often show up soon after eating eggs. Understanding them helps you know if eggs are the problem. Symptoms can range from mild discomfort to more severe reactions.
Digestive Problems
Digestive issues are common signs of egg intolerance. Diarrhea often occurs, leading to frequent, loose stools. Some people experience stomach cramps or pain. Bloating and gas may also develop after eating eggs. Nausea can happen, making you feel sick to your stomach. These symptoms usually start within a few hours of consumption.
Other Physical Discomforts
Egg intolerance can cause more than just stomach trouble. You might feel tired or weak after eating eggs. Headaches or migraines sometimes appear as a reaction. Skin problems like rashes or itching may develop. Some people notice swelling around the face or lips. These signs suggest your body is reacting negatively to eggs.
Distinguishing Allergy From Intolerance
Understanding the difference between egg allergy and intolerance is important. Both can cause digestive issues like diarrhea. Yet, their causes and effects vary greatly. Recognizing the signs can help manage symptoms effectively and avoid confusion.
Immune Response In Egg Allergy
Egg allergy triggers the immune system. The body mistakes egg proteins for harmful invaders. It releases chemicals like histamine to fight them. This causes allergic reactions such as hives, swelling, or even severe difficulty breathing. Diarrhea may also occur as part of this immune response. Allergies can be life-threatening and need immediate medical attention.
Digestive Discomfort In Intolerance
Egg intolerance involves the digestive system, not the immune system. The body struggles to break down certain egg components. This can lead to symptoms like stomach pain, gas, bloating, and diarrhea. Unlike allergies, intolerance rarely causes severe reactions. Symptoms usually appear slowly and depend on how much egg is eaten. Managing intolerance often means limiting egg intake to reduce discomfort.
When To Get Medical Help
Knowing when to seek medical help is important if eggs cause diarrhea or other digestive problems. Mild symptoms often improve with home care. Yet, some signs require prompt attention to avoid complications. Watch your body closely and do not ignore severe or lasting issues.
Emergency Symptoms
Seek immediate medical help if you experience severe abdominal pain. High fever above 101°F (38.3°C) is a warning sign. Blood in stool or vomit needs urgent evaluation. Signs of dehydration like dizziness, dry mouth, or fainting demand quick care. Rapid heartbeat and confusion are also emergencies.
Persistent Digestive Issues
See a doctor if diarrhea lasts more than two days. Ongoing cramping or bloating should not be ignored. Weight loss without trying is a concern. If diarrhea disrupts daily life, medical advice is essential. A healthcare provider can check for allergies or infections. Proper diagnosis helps guide safe treatment and diet changes.

Credit: drjockers.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Do Eggs Have A Laxative Effect?
No, eggs do not have a laxative effect. They are low in fiber and may cause constipation if eaten in excess without fiber. Eggs can help firm stools in some people with diarrhea but do not act as a laxative.
What Are The Symptoms Of Egg Intolerance?
Symptoms of egg intolerance include bloating, gas, stomach cramps, diarrhea, nausea, fatigue, headaches, and brain fog. These signs are digestive and non-immune based.
Why Can I Eat Hard Boiled Eggs But Not Scrambled?
You can eat hard boiled eggs but not scrambled due to differences in digestion and ingredient additives. Scrambled eggs often contain milk or butter, which may cause intolerance or allergies. Hard boiled eggs are simpler and easier to digest, reducing digestive discomfort for sensitive individuals.
What Foods Commonly Cause Diarrhea?
Foods that commonly cause diarrhea include spicy dishes, dairy products, fatty foods, artificial sweeteners, and high-fiber fruits like prunes. Some individuals react to gluten, caffeine, or contaminated food. Food intolerances and allergies, such as to eggs or lactose, can also trigger diarrhea.
Conclusion
Eggs do not usually cause diarrhea for most people. They are low in fiber and high in protein. This can sometimes lead to constipation, not diarrhea. Some people with sensitive stomachs or egg allergies may react differently. Eating eggs with fiber-rich foods helps balance digestion.
Drinking enough water also supports regular bowel movements. Always watch how your body responds to eggs. Consult a doctor if you notice ongoing stomach problems. Eggs can be part of a healthy diet when eaten wisely.
